Field Data - Currents
To determine the current velocity
in relation to the water inflow controlled by an upstream weir,
a number of acoustic currentmeters were deployed within the
two lakes.
| The instruments,
which were moored at the bottom
of the lake, are recording all
three dimensions of the current
pattern (2 horizontal and 1 vertical
component). The acoustic currentmeters
applied for this survey are using
the so-called “Doppler Effect” to
determine the current velocity
and direction of tiny particles
moving with the currents. The
currentmeters are recording with a very high
frequency so that the evaluation
of the recorded data has to be
done with statistical methods. |
|
ADCP
(Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)
|
 |

|
Acoustic
currentmeter (ADV) |
Deployment
of ADCP |
Apart of the point measurements (time series) carried out with
two moored ADV (Acoustic Doppler
Velocimeter) a number of short-term current measurements were carried
out with a mobile ADV. These measurements
were carried out close to the surface
at different locations and with different inflow volumes (see red
dots). The ADCP, which was
moored close to the deepest part
of the Mühlenteich, provided
a vertical profile of the three-dimensional
current pattern, measuring from the bottom-mounted instrument up
to the water surface. This
vertical current profile is divided
in a number of cells or layers. The number of these cells is a measure
for the vertical resolution.
It can be preselected before deployment.
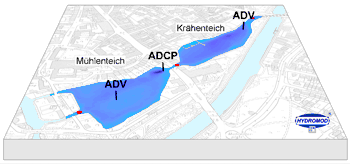 |
Figure:
Location map of
the currentmeter moorings and mobile current measurements.
ADV – Point measurements
ADCP – Vertical current profile |
The current data recorded during the survey were used for the validation
of the model system.
The figures below show partial results of the current measurements.
Depending on the inflow volume (green line = inflow) and measuring
location each record reveals a significant current pattern.
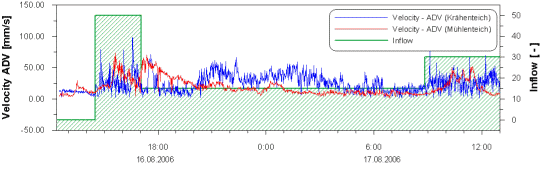 |
Figure: Graph of the time series of
current measurements carried
out in the Krähenteich
(blue line) and in the Mühlenteich
(red line). From the Mühlenteich
data it clearly can be seen,
that its curve is delayed in
comparison with the Krähenteich
data.
|
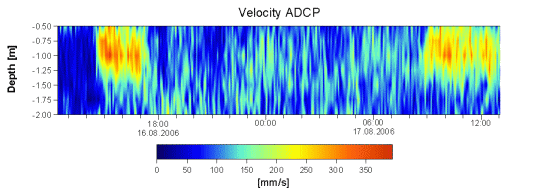 |
Figure: Current
Velocity - The ADCP measurements
(vertical current
profile) were carried out in
the vicinity of the deepest
part of the Mühlenteich.
With an inflow ratio of 50
% at the controlling wear
(about 3.6 m³) a maximum
current velocity of 40 cm/s
was recorded.
Furthermore it can be seen
that variations of the current
pattern are clearly related
to the changes of inflow volumes
and that the higher current
velocities are restricted to
the upper layer reaching down
to 1.5 m water depth.
|
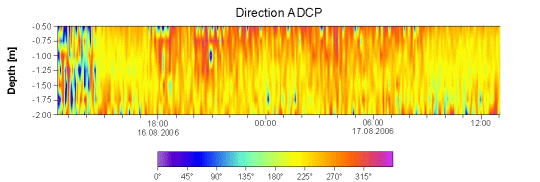 |
| Figure: Current direction – The
time series of the current direction
clearly reveals that the dominating
current direction at the ADCP
location (see figure above) is
to the southeast. |
next ...


